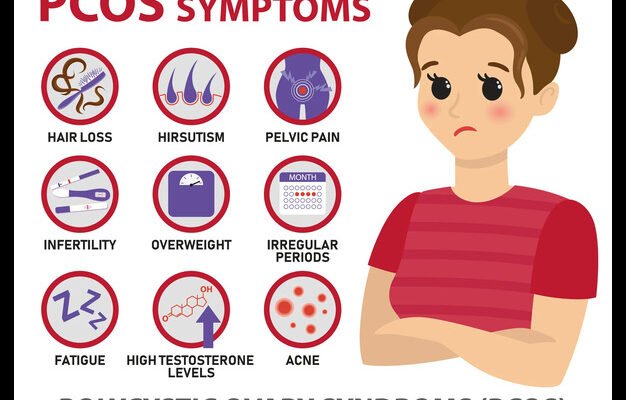
Introduction to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Imagine waking up every day, not knowing if your body will cooperate with you. This is a reality for millions of women worldwide who suffer from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Affecting approximately 1 in 10 women of childbearing age, PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders. Despite its prevalence, it remains widely misunderstood and often misdiagnosed, leading to a frustrating and challenging journey for those affected.
The purpose of this blog is to shed light on how PCOS disrupts hormone levels, particularly focusing on high testosterone levels and their impact. By understanding the intricacies of this condition, women can better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Understanding PCOS’s Impact on Hormone Levels
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome isn’t just about irregular periods or fertility issues. At its core, PCOS is a hormonal imbalance that wreaks havoc on various aspects of a woman’s health. One of the key hormones affected by PCOS is testosterone. While testosterone is often labeled as a “male” hormone, it plays a crucial role in female bodies too, just in smaller amounts.
In women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, the ovaries produce more testosterone than usual. This hormonal imbalance causes a cascade of symptoms that can be both physically and emotionally draining. Understanding the role of testosterone in PCOS is essential to grasp the full scope of the condition.
Symptoms of High Testosterone in PCOS
High testosterone levels in women with PCOS can manifest in several ways. These symptoms can be distressing and affect self-esteem and overall well-being.
Irregular Periods
One of the most common signs of PCOS is irregular menstrual cycles. High testosterone levels interfere with the normal ovulation process, leading to infrequent or prolonged periods. Some women may experience fewer than eight periods a year, while others might go months without menstruating.
Acne and Oily Skin
Testosterone stimulates the production of sebum, an oily substance that can clog pores and lead to acne. Women with PCOS often struggle with persistent acne that is resistant to conventional treatments. The excess oil can also make the skin appear greasy and exacerbate skin issues.
Unwanted Hair Growth
Hirsutism, or excessive hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair, is another hallmark of high testosterone in PCOS. Women may notice coarse, dark hair on their face, chest, back, and abdomen. This can be particularly distressing and impact self-confidence.
Health Risks Associated with High Testosterone in PCOS
Beyond the visible symptoms, high testosterone levels in PCOS can pose serious health risks. These risks highlight the importance of early diagnosis and proper management of the condition.
Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. High testosterone levels further exacerbate insulin resistance, creating a vicious cycle.
Cardiovascular Issues
Elevated testosterone levels in women with PCOS are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. These women are more likely to have high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and other risk factors for heart disease. Monitoring and managing these risk factors is crucial for long-term health.
Endometrial Cancer
Irregular periods and lack of ovulation can lead to a build-up of the endometrial lining in the uterus. Over time, this can increase the risk of endometrial cancer. Managing hormone levels and ensuring regular menstrual cycles can help reduce this risk.
Managing High Testosterone in PCOS
While there is no cure for PCOS, several strategies can help manage high testosterone levels and alleviate symptoms. A combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and natural remedies can make a significant difference.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the foundation of managing PCOS. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate hormone levels. Losing even a small amount of weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce testosterone levels.
Medication
Several medications can help manage high testosterone levels in PCOS. Birth control pills are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and lower androgen levels. Anti-androgen medications, such as spironolactone, can reduce excessive hair growth and acne.
Natural Remedies
Some women find relief from PCOS symptoms through natural remedies. Supplements like inositol and spearmint tea have shown promise in reducing testosterone levels and improving insulin sensitivity. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Insights from Experts and Real-Life Experiences
Hearing from experts and women who live with PCOS can provide valuable insights and support. Dr. Jane Smith, an endocrinologist specializing in women’s health, emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing PCOS. “Addressing PCOS requires collaboration between gynecologists, endocrinologists, and nutritionists to create a personalized treatment plan,” she says.
Real-life experiences also shed light on the challenges and triumphs of living with PCOS. Sarah, a 28-year-old woman diagnosed with PCOS, shares her story. “It took years to get a proper diagnosis, but once I started managing my symptoms with lifestyle changes and medication, I felt like I had control over my body again,” she says. “Joining a support group made a huge difference; knowing I’m not alone in this journey is incredibly empowering.”
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Support
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing PCOS and preventing long-term health complications. If you suspect you have PCOS or experience symptoms like irregular periods, acne, or unwanted hair growth, seek medical advice. Getting a comprehensive evaluation can help tailor a treatment plan that suits your needs.
Support is equally important. Joining a PCOS support group or connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide emotional comfort and practical advice. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you.
Conclusion
Navigating the hormonal maze of PCOS and high testosterone can be challenging, but understanding the condition and taking proactive steps can make a world of difference. By managing symptoms through lifestyle changes, medication, and natural remedies, women with PCOS can improve their quality of life and reduce health risks. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential, as is seeking support from healthcare providers and the community. Remember, you have the power to take control of your health and well-being.
Stay informed, stay healthy, and know that you are not alone in this journey.
Read also : Blood Cancer and Tattoos: Examining the Current Research